The Tea Quality and Risk Assessment Innovation Team of the Tea Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) revealed the uptake and transport patterns of pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) and their N-oxides (PANOs) and their degradation mechanisms in tea tree (Camellia sinensis L.).
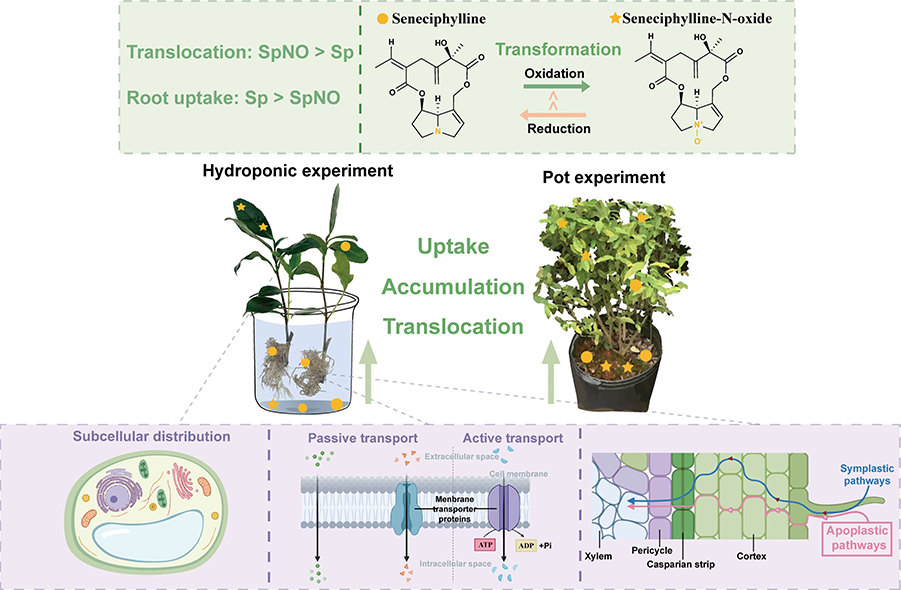
Recently, the Tea Quality and Risk Assessment Innovation Team of the Tea Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) revealed the uptake, accumulation, translocation and transformation of seneciphylline (Sp) and seneciphylline-N-oxide (SpNO) by ‘Uptake, accumulation, translocation and transformation of seneciphylline (Sp) and seneciphylline-N-oxide (SpNO) by the risk assessment of the pollutants in tea’. The research results were presented as ‘Uptake, accumulation, translocation and transformation of seneciphylline (Sp) and seneciphylline-N-oxide (SpNO) by Camellia sinensis L.’, respectively. Camellia sinensis L.”, ’Insight into pyrrolizidine alkaloids degradation and the chemical structures of their degradation products using ultra high performance Insight into pyrrolizidine alkaloids degradation and the chemical structures of their degradation products using ultra high performance liquid chromatography and Q-Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometry’ have been published in the journals Environmental International and Journal of Hazardous Materials, respectively.
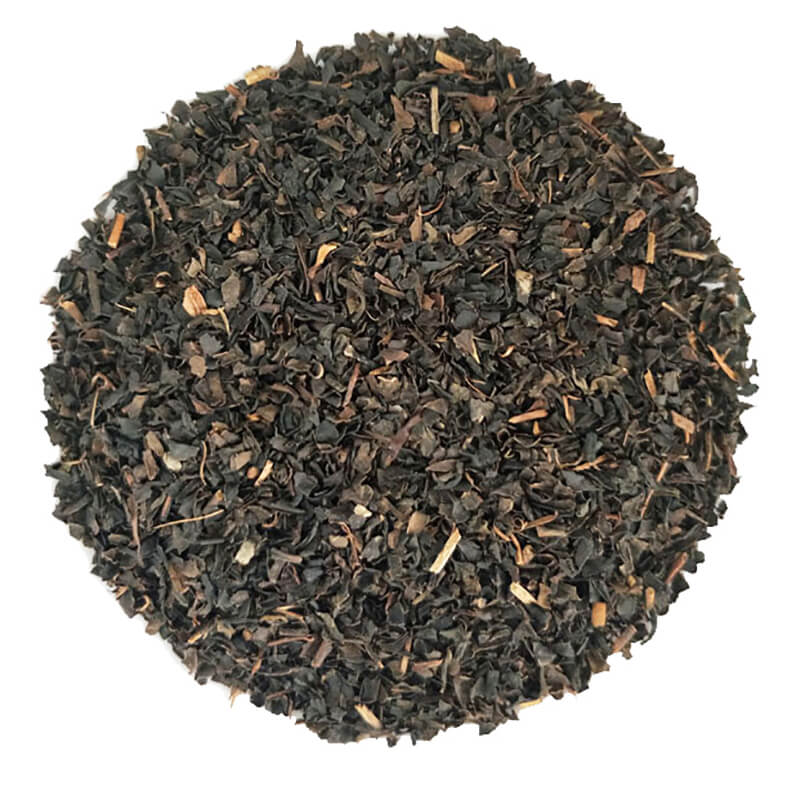
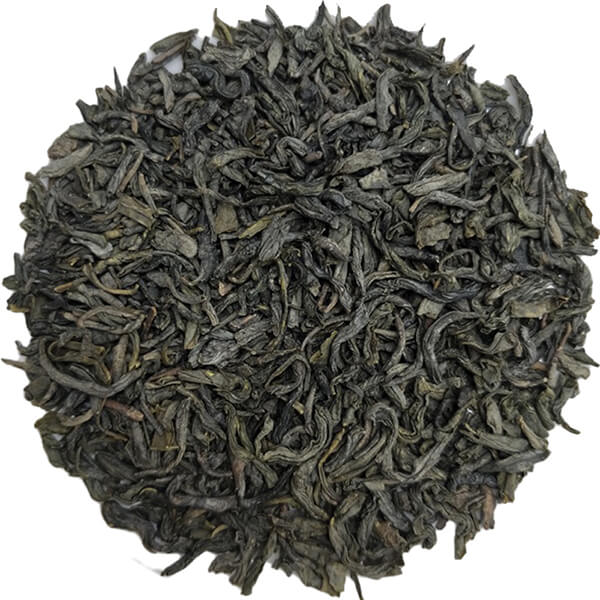
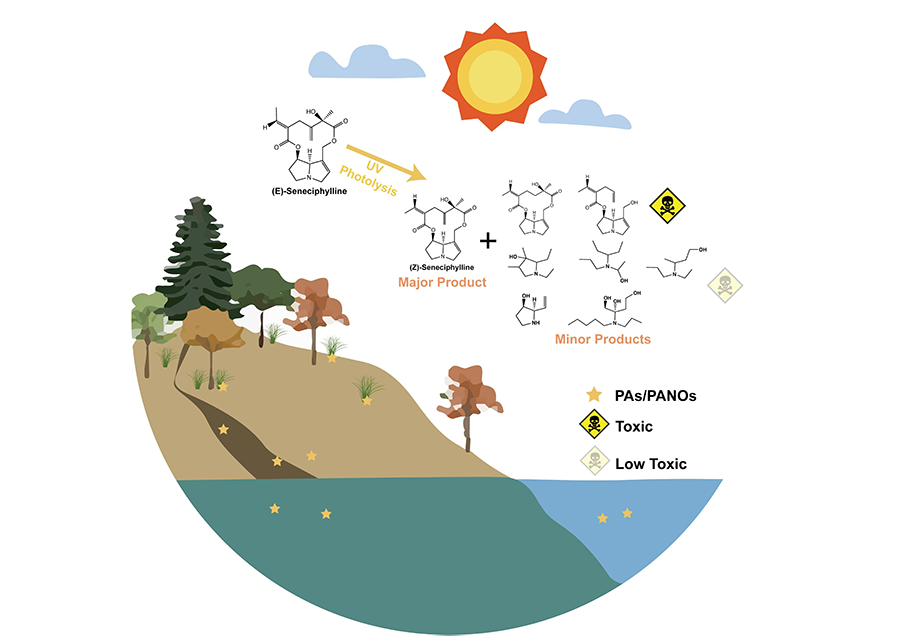
PAs/PANOs are plant toxins, of which more than 660 species have been identified in more than 6000 plants. PAs/PANOs are a food safety contaminant of great concern because of their potential health risks to human beings, and they are subject to stringent restrictions by the European Union (EU) and other countries, which has become an additional risk factor for the export of agricultural products, such as tea, from China. However, the contamination pathways of PAs/PANOs in tea and their degradation behaviours are still unclear, which is not conducive to the risk assessment and scientific control of PAs/PANOs in tea. In this study, ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-electrostatic field orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q Exactive Orbitrap-MS) techniques were used to reveal the uptake and transport patterns of representative PAs, senecio pheromones (Sp) and their nitrogen oxides (SpNOs), in tea, as well as 15 PAs/PANOs, and identified the chemical structures of the degradation products. It was found that the root system of tea tree absorbed Sp/SpNO efficiently through the active transmembrane pathway; there were differences in the uptake and transport of Sp and SpNO, with the former mainly concentrated in the roots and the latter more easily transported to the above-ground parts; and there was a phenomenon of reduction of SpNO to Sp in the tea tree. In addition, it was found that the photolysis of PAs/PANOs was faster under alkaline conditions, and the degradation rate was related to the structure of the compounds, and the degradation products mainly consisted of isomers with similar toxicity and secondary by-products with lower toxicity.